What is the difference between 220-volt used by Europeans and 120/240-volt used in the United States?
The main difference between 220-volt used in Europe and 120/240-volt used in the United States is the voltage level. 220-volt is a higher voltage level than 120/240-volt. This means that devices designed to run on 220-volt will consume less current to produce the same amount of power as a device designed to run on 120/240-volt. This can lead to more energy-efficient and potentially smaller devices. Additionally, the plug and socket configurations used in Europe and the United States are different, so devices designed for one region may not be compatible with the electrical outlets in the other region without an adapter.
Can I connect a solar inverter designed for 220-volt to a 120/240-volt grid?
A solar inverter designed for 220-volt will not be compatible with a 120/240-volt grid without a voltage step-down transformer. The transformer is needed to reduce the 220-volt output of the inverter to the 120/240-volt standard used in the United States.
It’s important to note that, even with a transformer, the inverter may not be compatible with the grid in the US, as it may have different safety and communication standards.
It is recommended to use an inverter that is specifically designed to work with the grid voltage and standards in the United States to ensure proper operation, safety, and compatibility with the grid.
How an autotransformer converts the output of a 220-volt solar inverter to a 120/240-volt line?
An autotransformer is an electrical transformer with only one winding, which is used to adjust the voltage level of an alternating current (AC) power source. In this case, an autotransformer can be used to convert the output of a 220-volt solar inverter to the 120/240-volt standard used in the United States.
The autotransformer works by tapping into the single winding at different points. The output voltage is determined by the ratio of the turns between the input and the output. For example, if the autotransformer has a ratio of 1:2, then an input voltage of 220 volts will be stepped down to 110 volts at the output.
The autotransformer connects to the 220-volt output of the solar inverter and then to the 120/240-volt grid, it uses a winding that is common to both the input and output to transfer power. It adjusts the voltage level by connecting to different points on the winding. In this way, the autotransformer effectively “steps down” the voltage from 220 volts to 120/240 volts.
It’s important to note that the autotransformer alone may not be sufficient to connect the inverter to the grid and there may be other necessary equipment and safety measures that need to be in place. It is also important to use a properly sized and rated autotransformer to ensure safe and efficient operation. It is recommended to consult a professional electrician or a solar system designer/installer to properly connect the inverter to the grid.
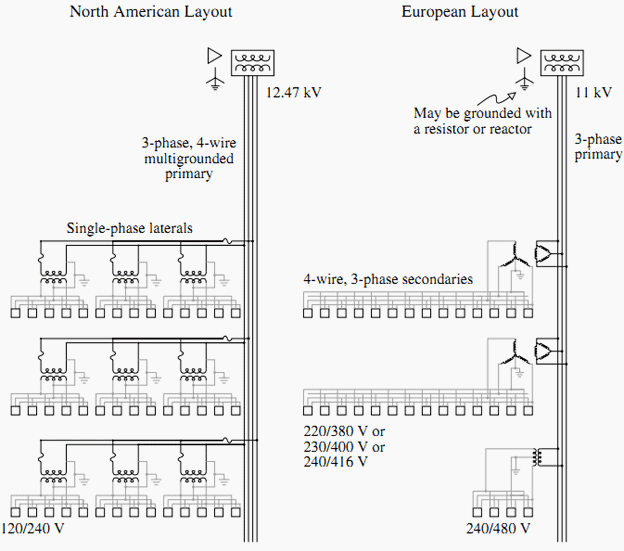
Explain to me the difference between the American 3-phase, 4-wire delta layout, and the European 3-phase, 3-wire Y layout.
The American 3-phase, 4-wire delta layout and the European 3-phase, 3-wire Y layout are different ways of connecting three-phase electrical power systems.
In the American 3-phase, 4-wire delta layout, three wires are used to carry the three phases of electrical power, and a fourth wire is used as a neutral or grounding wire. The three phases are connected in a closed loop, or “delta” configuration, with each phase 120 degrees apart. This layout is commonly used in the US and Canada, and it is particularly suitable for large commercial and industrial loads.
On the other hand, in the European 3-phase, 3-wire Y layout, three wires are used to carry the three phases of electrical power, and there is no neutral wire. The three phases are connected in a “Y” configuration, with each phase 120 degrees apart. This layout is commonly used in Europe, Asia, and other parts of the world, and it is particularly suitable for residential and small commercial loads.
The main difference between these two layouts is the presence of a neutral wire in the American layout, which allows for a more efficient use of energy by supplying the unbalanced loads and connecting the neutral conductor to ground for safety. The European layout, however, has no neutral wire, so the unbalanced loads have to be supplied by the line conductors and may create an unbalanced current in the system.
Another difference is that the American layout is more suitable for large commercial and industrial loads, while the European layout is more suitable for residential and small commercial loads.